Understanding intellectual property rights
Here you will find information on Intellectual Property (IP) rights and related ETH policies. Please note that some IP rights mentioned (e.g. trademarks) are not managed by ETH transfer.
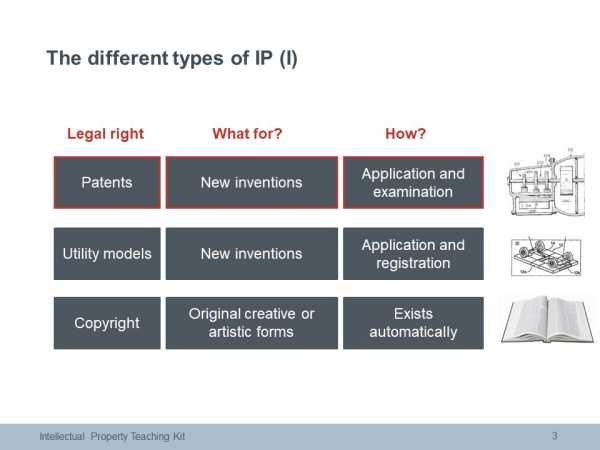
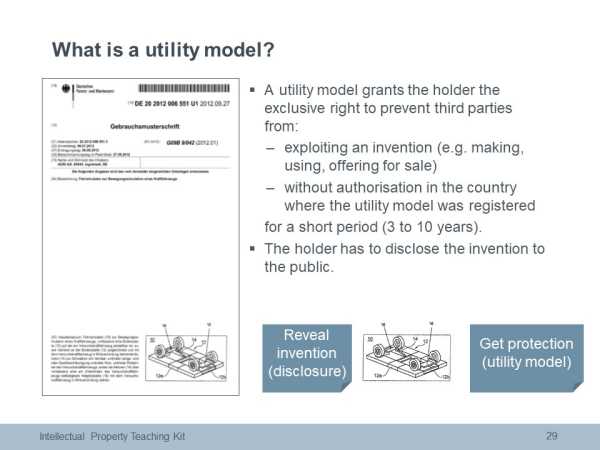
Utility models
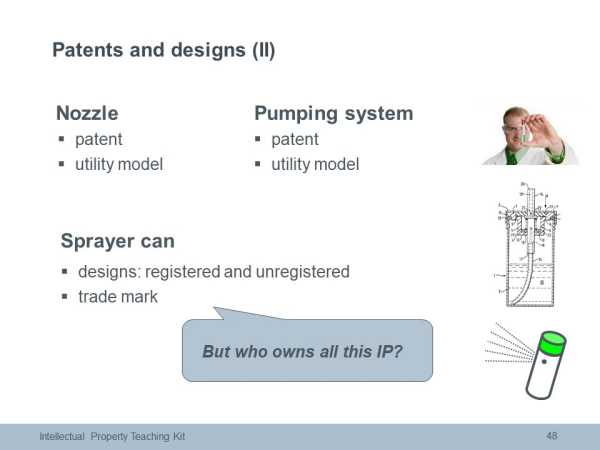
Utility models offer simpler protection, for a shorter period of time, but are usually registered and published much more quickly than patents. In most countires, utility models are registered without examination, within a few months of the filing application. Utility models are available in for example Austria, China, Germany and Japan. They are not available for example in Canada, the UK, the USA or Switzerland.
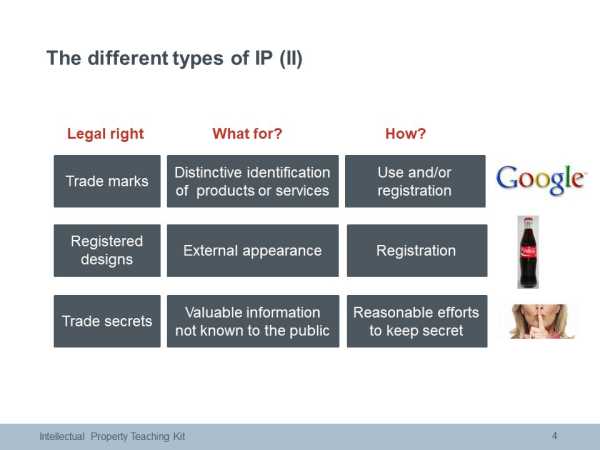
Trade marks
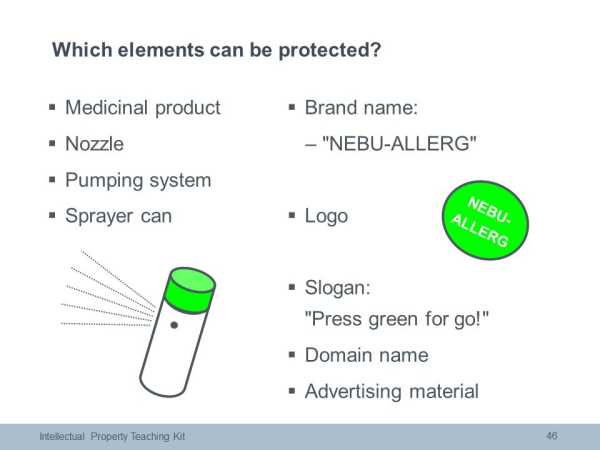
A trademark consists of any signs capable of distinguishing goods or services of one firm or company from those of another. Trade marks serve to indicate the commercial source or origin of the products and services they relate to. Moreover, trade marks may fulfil other functions such as advertisement or goodwill. The many different types of trade mark include word marks, figurative marks and colour and shape marks. Trade mark protection is limited to the territory where the mark is registered. Unlike other IP rights, trade marks can be renewed indefinitely. Each renewal adds ten years of protection.
Design
A design is the outward appearance of the whole or parts of a product. A product can be any industrial or handicraft item. Examples of design features include lines, colours and shapes. Examples of the products to which they are applied or in which they are incorporated include packaging and logos. There are two requirements for protection: it must be new and have individual character. Design protection has two forms: registered (max. 25 years) and unregistered (3 years). Unregistered designes (Unregistered Community Designs) can be useful for products and designs that have an exceptionally short lifespan.
Trade Secrets
To become a trade secret the information must be confidential; it should have commercial value because of its confidentiality; and the trade secret holder should have made reasonable efforts to keep it confidential. Non-disclosure agreements help keep information exchanged with customers or potential partners confidential. Access can be restricted to those employees with a need to know the information. More generally, data can be encrypted (in particular if it is sent over the internet) and entry into certain areas of a manufacturing plant controlled.
For more information consult the website of the external page European Patent Office and/or download their external page IP Basics Teaching Kit (preview below).